Leave Your Message
High performance computing (HPC) relies heavily on the efficiency of specialized hardware. Among these, server GPU cards stand out as essential for accelerating computational tasks. According to a recent industry report by Jon Peddie Research, the data center GPU market is projected to reach $38 billion by 2026, emphasizing the increasing reliance on these powerful components.
Server GPU cards facilitate advanced workloads in fields such as artificial intelligence, scientific simulations, and big data analytics. As organizations seek to enhance processing capabilities, the significance of choosing the right GPU becomes paramount. For instance, NVIDIA’s A100 Tensor Core GPUs have been adopted widely in enterprise environments to improve machine learning performance. However, identifying the best options can be challenging amid rapid technological advancements and evolving industry needs.
Considering factors such as performance, memory, and compatibility is crucial. Yet, many businesses overlook the importance of proper integration with existing systems. In doing so, they often miss out on maximizing efficiency and performance. Continuous innovation in server GPU cards means that staying informed is vital for keeping pace with HPC requirements.

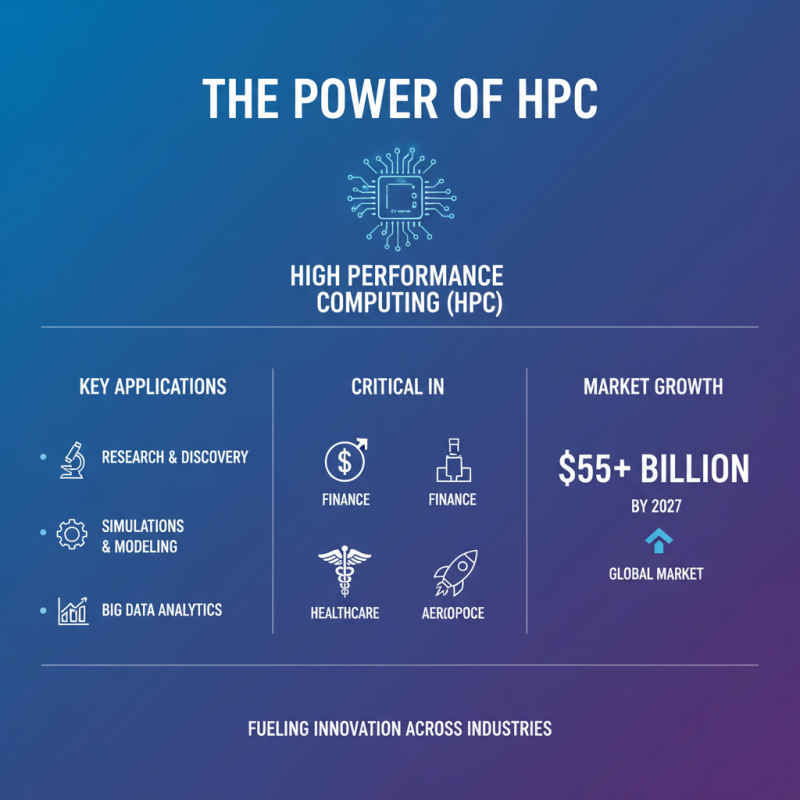
High Performance Computing (HPC) has become pivotal in various fields. Research, simulations, and data processing all depend on HPC. The demand for complex computations is growing. Industries like finance, healthcare, and aerospace are leading the charge. In fact, a recent industry report noted that the HPC market will exceed $55 billion by 2027.
The requirements for HPC systems are unique. They need advanced processing power and fast memory access. Achieving efficiency is crucial. Data throughput and low latency are key considerations. More cores and enhanced parallel processing capabilities are necessary. However, many organizations struggle with the cost and complexity of deploying such powerful systems.
**Tips:** Investing in scalable architectures can help. Consider cloud-based solutions for flexibility. Regularly assess your requirements to avoid overspending on unnecessary capabilities. Remember, what works now may not fit future needs. Continuous evaluation is essential. Balancing performance and cost-effectiveness should be a priority. Use benchmarking tools to gauge system effectiveness over time.
When selecting server GPU cards for high-performance computing (HPC), several key features come into play. Performance, memory bandwidth, and power efficiency are top priorities. A recent industry report highlights that the right GPU can improve computational speed by up to 50% compared to previous generations. Memory size often dictates how many calculations can be handled simultaneously. Often, GPUs with 16GB or more memory are preferred in HPC environments. This allows for larger datasets, crucial for tasks like AI model training.
Thermal management is another critical aspect. The processing power of GPUs generates heat, which can lead to throttling if not managed well. Poor cooling solutions can reduce performance by 10-20%, as reported in several studies. Power consumption also matters. Some high-end GPUs can consume over 300 watts. This impacts operational costs significantly. Choosing a GPU that balances performance and power can save money in the long run. Balancing these needs requires careful consideration and reflection. Each project may have unique requirements that complicate decision-making. Emphasizing flexibility and adaptability in these choices is vital for achieving optimal performance.
This chart displays the performance index of the top 10 server GPU cards suitable for high performance computing (HPC). The performance index is a qualitative measure combining various factors including processing power, memory bandwidth, and energy efficiency.
In the realm of high-performance computing, selecting the right server GPU card is crucial. Server GPUs are designed to handle massive computations. They excel in AI, machine learning, and data processing tasks. Each card offers unique specifications that cater to different workloads.
Many server GPU cards boast impressive memory sizes, some providing up to 48 GB of VRAM. This is essential for workloads that require high memory bandwidth. Performance reviews often highlight the processing capabilities, with some cards achieving thousands of operations per second. However, not all perform equally under pressure. Users may find certain models overheating during extended use, affecting reliability.
Power consumption is another critical factor. Some GPUs consume more energy, leading to increased operational costs. Balancing performance and efficiency creates a challenge. Reflection is necessary here; a powerful GPU may not always be the best choice for every computing need. The ideal server GPU card should align with specific application requirements, rather than just specifications on paper.
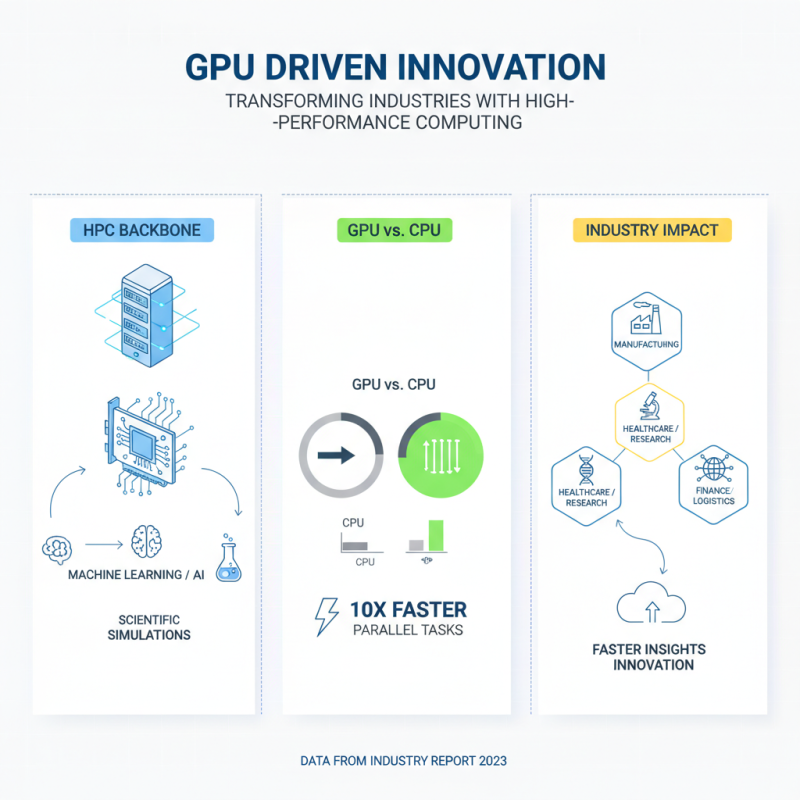
High performance computing (HPC) is transforming various industries. The backbone of HPC systems is often the GPU. Server GPUs play a crucial role in processing vast amounts of data quickly. According to a recent industry report, GPUs can outperform traditional CPUs by tenfold in parallel tasks. This is vital for applications like machine learning and scientific simulations.
A comparative analysis reveals distinct performance metrics among leading server GPUs. For instance, GPUs with higher memory bandwidth demonstrate significantly better throughput. Research indicates that a bandwidth exceeding 800 GB/s is essential for optimal data-intensive applications. However, inefficiencies still exist in GPU integration with existing infrastructures. Many organizations struggle with lack of compatibility and high costs, limiting their ability to leverage the full potential of these powerful chips.
Thermal management poses another challenge. GPUs generate substantial heat during operation. Proper cooling systems are necessary to maintain performance. Studies reveal that poor thermal design can reduce GPU efficiency by nearly 30%. While selecting GPUs for HPC needs, these factors should not be overlooked. Balancing performance, cost, and cooling solutions is crucial for maximizing ROI in HPC investments.
The landscape of server GPU technology is evolving rapidly. Companies are increasingly investing in AI and machine learning applications. This trend necessitates more powerful and efficient GPU cards. Advanced models are being developed to handle larger datasets and complex computations. However, achieving optimal performance remains a challenge. Balancing power efficiency with processing capabilities is crucial.
Emerging technologies, such as stackable GPU designs, promise significant improvements. These innovations aim to enhance communication between GPUs, minimizing latency. Moreover, the integration of AI-driven resource management systems could optimize workload distribution. Still, there are hurdles to overcome. Compatibility issues and software adaptations can hinder widespread adoption. Future developments must focus on resolving these challenges.
As server GPU architectures become more sophisticated, new usage scenarios will arise. Researchers and organizations will likely seek versatile solutions for diverse HPC tasks. However, keeping costs manageable is essential for broader implementation. The pressure to innovate must be balanced with the need for stability. This dynamic environment will shape how we approach high-performance computing in the years to come.
